The structure and principle of refrigerator condenser
1. The structure of the condenser in the refrigerator
The condenser is the heat dissipating part of the refrigerator. It is usually located on the back of the refrigerator. According to the different design of the condenser, the condenser can be divided into two types: exposed type and built-in type, as shown in the figure below.
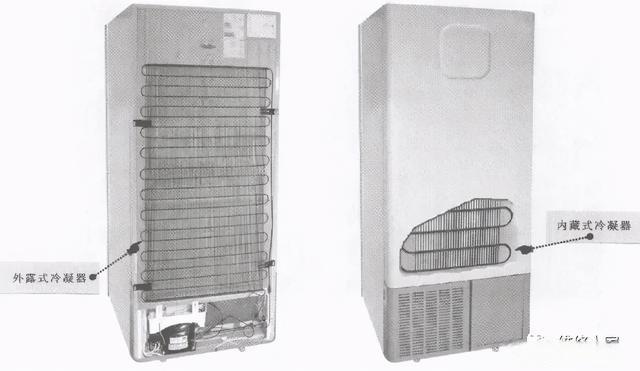
1. Exposed condenser
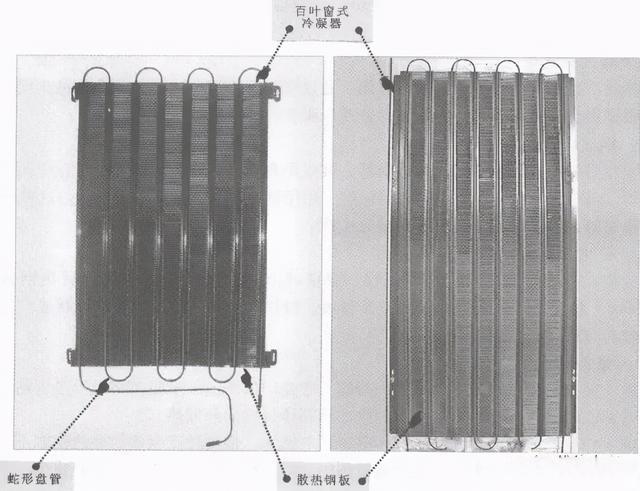
The exposed condenser is directly fixed on the back of the refrigerator, and is connected with the refrigeration pipeline of the refrigerator through a connecting pipe. Exposed condensers can be divided into steel coil condensers and louver condensers according to different heat dissipation methods.
(1) Wire coil condenser
The wire-coil condenser is also called the wire-tube condenser. Its serpentine coil is made of coiled and welded copper-plated sheet steel, and steel wires with a diameter of 1.5 ~ 2mm are uniformly welded on both sides of the coil. Use steel wire to dissipate heat, as shown in the figure below. The condenser is small in size, light in weight, good in heat dissipation, and convenient for mechanized production.

(2) Louvered condenser
The louvered condenser is to tightly embed, expand or spot weld the coil on the heat dissipation steel plate of the louver-shaped air hole, as shown in the figure below. The coil pipe is usually made of red copper (pure copper) pipe, and the heat dissipation steel plate is made of ordinary carbon steel plate. This kind of condenser has a relatively simple structure, but its heat dissipation effect is poor.
2. Built-in condenser
At present, most refrigerators use a built-in condenser, which uses extruded or glued aluminum foil to stick the serpentine coil on the back of the refrigerator box or the inside of the thin steel plate on the side, and use the outer wall of the refrigerator box to outward Heat dissipation.
The built-in condenser has the advantages of small footprint and not easy to be damaged, but the heat dissipation performance of this condenser is not as good as that of the exposed condenser, and because the condenser is located in the refrigerator box, the maintenance of this condenser is also relatively good. trouble. The figure below shows the structure diagram of the built-in condenser.

3. Air-cooled condenser
An air-cooled condenser is used in large refrigerators. Its structure is shown in the figure below. It is composed of pure copper tubes and fins. The pure copper tubes are welded in the fins and made into a rectangular parallelepiped together with the fins. In the wall of the box. This kind of condenser has a compact structure, high heat dissipation efficiency, and a large heat dissipation capacity. The forced convection cooling method (air-cooled heat dissipation) is usually used to improve the heat dissipation efficiency.

Second, the working principle of the condenser
The figure below shows the working principle of the refrigerator condenser. The condenser is also called a radiator. Its air inlet pipe is connected to the compressor outlet. The high-temperature and high-pressure refrigerant gas processed by the compressor enters the condenser from the air inlet, and the condenser’s air outlet pipe is connected to the drying filter. The refrigerant is connected to the condenser, and the refrigerant, which has been cooled by the condenser, becomes liquid, filtered by the filter drier, throttling and reducing the pressure by the capillary tube, and then sent to the evaporator.
Its function is to transfer the high-temperature and high-pressure refrigerant gas processed by the compressor to the surrounding air through heat exchange, and then cool it into a liquid state to achieve heat exchange.



